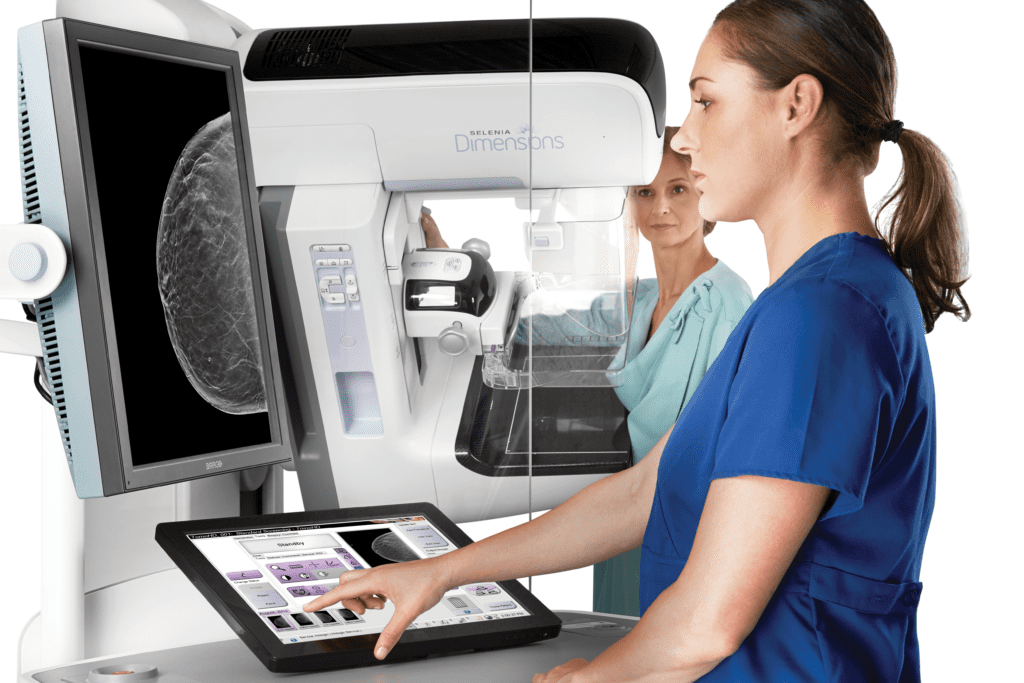
Breast Cancer Screening
Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women regardless of race or ethnicity. One in 8 women in the United States will develop invasive breast cancer. 85% of breast cancers occur in women with no family history. Studies have shown that screening mammograms save lives, reducing mortality from breast cancer by 20-40%.
Recommendations for when to start screening and how often to screen vary by different medical societies.
- The American College of Radiology (ACR) recommends annual screening mammograms at age 40 for women at average risk for developing breast cancer.
- The American Cancer Society recommends annual screening mammography for women at age 45 and possibly earlier at age 40 based on a discussion with their doctor.
- It is recommended that patients with strong family histories of breast cancer consult with their doctors for risk assessment as earlier screening is often recommended.


General Ultrasound
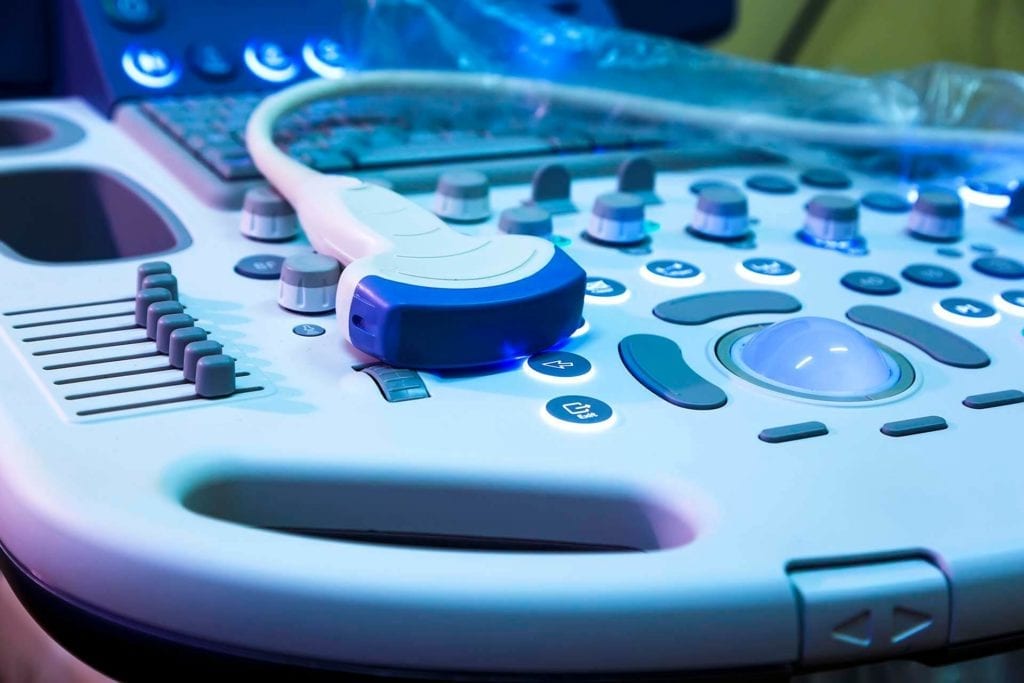


In addition to breast ultrasound, additional ultrasound exam types are also performed at the Women's Imaging Center. Ultrasound (sonography) utilizes sound waves to produce images of different body parts. Ultrasound exams produce no radiation to patients and are therefore preferred as the initial tests when possible depending on the area being evaluated, especially in young patients and children.
Preparation:
You should wear comfortable, loose-fitting clothing for your ultrasound exam.
Preparation protocols depend on the type of ultrasound you are having. You will be provided with specific instructions when scheduling your exam. Examples include:
- For a study of the abdomen, patients are asked to avoid eating for 6 to 8 hours before the test.
- For ultrasound of the kidneys or pelvis, you may be asked to drink four to six glasses of liquid about an hour before the test to fill your bladder.
For additional information about specific tests, please follow the links below:
Abdominal Ultrasound
Carotid Ultrasound
Obstetrical Ultrasound
Pelvic Ultrasound
Scrotum Ultrasound
Thyroid Ultrasound
Vascular Ultrasound
Venous Ultrasound
OB Sonograms
Obstetric sonograms are ultrasound studies that specifically evaluate the baby (fetus) and maternal organs during pregnancy. Sound waves are used to produce real-time images without ionizing radiation. The test is noninvasive and has no known harmful effects.
Additional information may be found at Radiology.org.

 (360) 428-7275
(360) 428-7275




